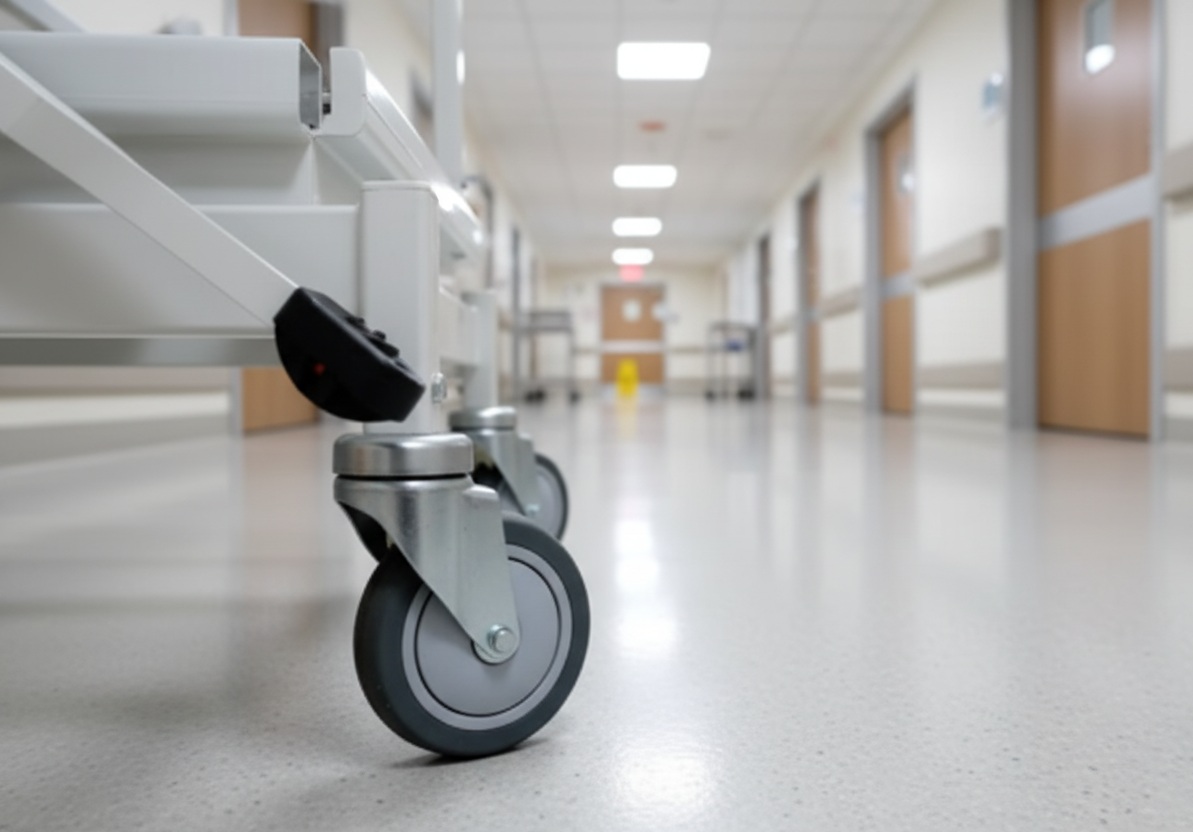




Hospital bed castors are small parts, but they decide how a bed behaves in daily use. If wheels glide smooth, staff move quicker and patients feel secure. When beds roll at the wrong time, accidents happen. That’s where locking mechanisms come in. They freeze the bed when it must stay still, and they guide it when it must move straight down a corridor.
On our site, you’ll find full details in the Hospital Bed Castor section. These aren’t just wheels—they are safety tools.
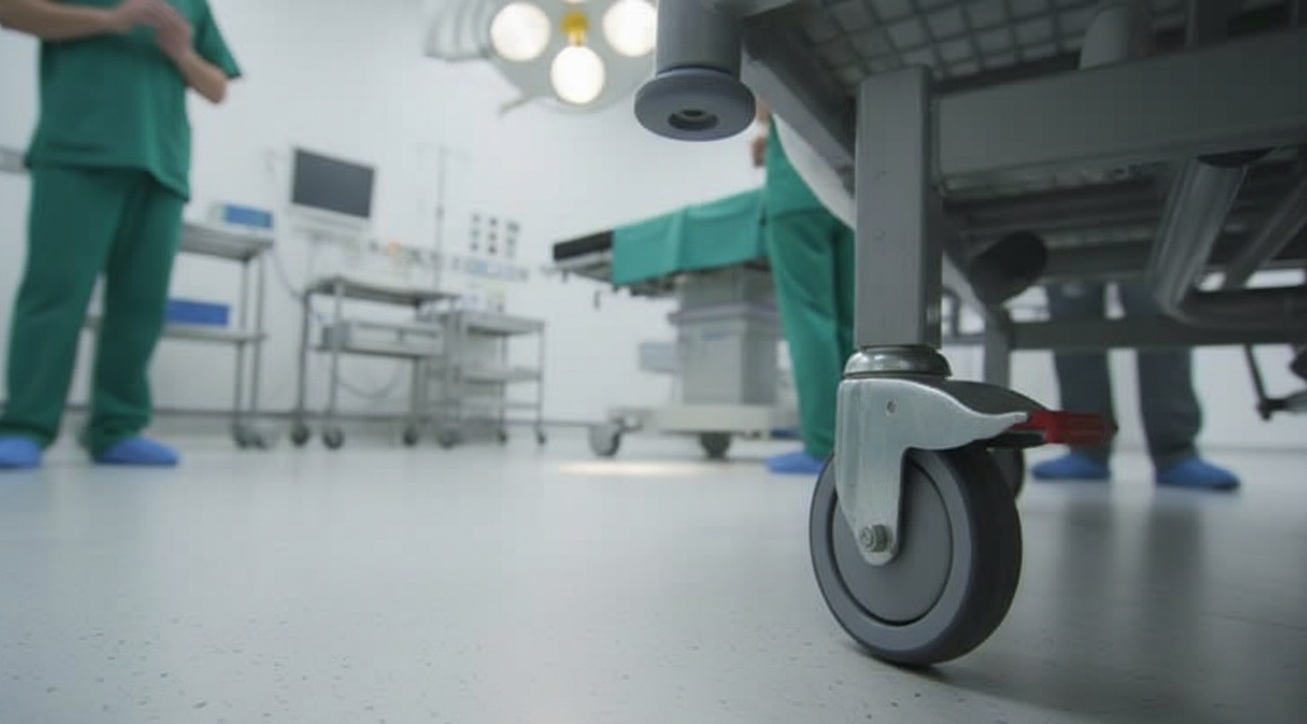

Let’s picture a nurse pushing a bed into an elevator. Without locks, the bed may slide back on its own. A total-lock system stops both rolling and swiveling. That makes the elevator ride safe.
In contrast, when pushing down a long hallway, a directional lock keeps one wheel aligned. The bed tracks straight instead of drifting side to side. This makes moving heavy loads lighter and cuts wasted effort.
Table: Common locking types and their uses
| Locking Type | What it Does | Best Scenario |
|---|---|---|
| Total lock | Stops rolling + swiveling | Parking a bed, elevator use, bedside care |
| Directional lock | Keeps one or more wheels straight | Long hallway transport |
| Neutral / free roll | Wheels move freely | When bed needs maximum maneuverability |
Studies show that smart caster design reduces strain on staff arms, shoulders, and backs. Push-pull force goes down when wheels lock correctly before turning or parking. In other words, locking mechanisms protect caregivers too, not just patients.
Healthcare facilities talk about “reducing musculoskeletal load” in procurement meetings. That’s the black-box term, but in practice, it means fewer injuries and faster shifts.

Beds roll even on flat floors. Add a patient, an IV pole, or a monitor, and the weight makes control harder. A bed without locked wheels may drift if someone leans on it. That drift can lead to falls, collisions, or just wasted time.
Regulatory bodies even publish guidance: always keep the bed in lowest position and wheels locked when not moving. Hospitals use this as standard operating procedure.
Every buyer knows procurement is not only about price. Compliance with safety standards matters. A hospital bed with proper locking castors meets international norms. It protects the facility from liability and improves audit scores.
For distributors and importers, this is a selling point. When you show your clients that your hospital bed castors meet safety standards, you’re not only selling wheels—you’re selling peace of mind.

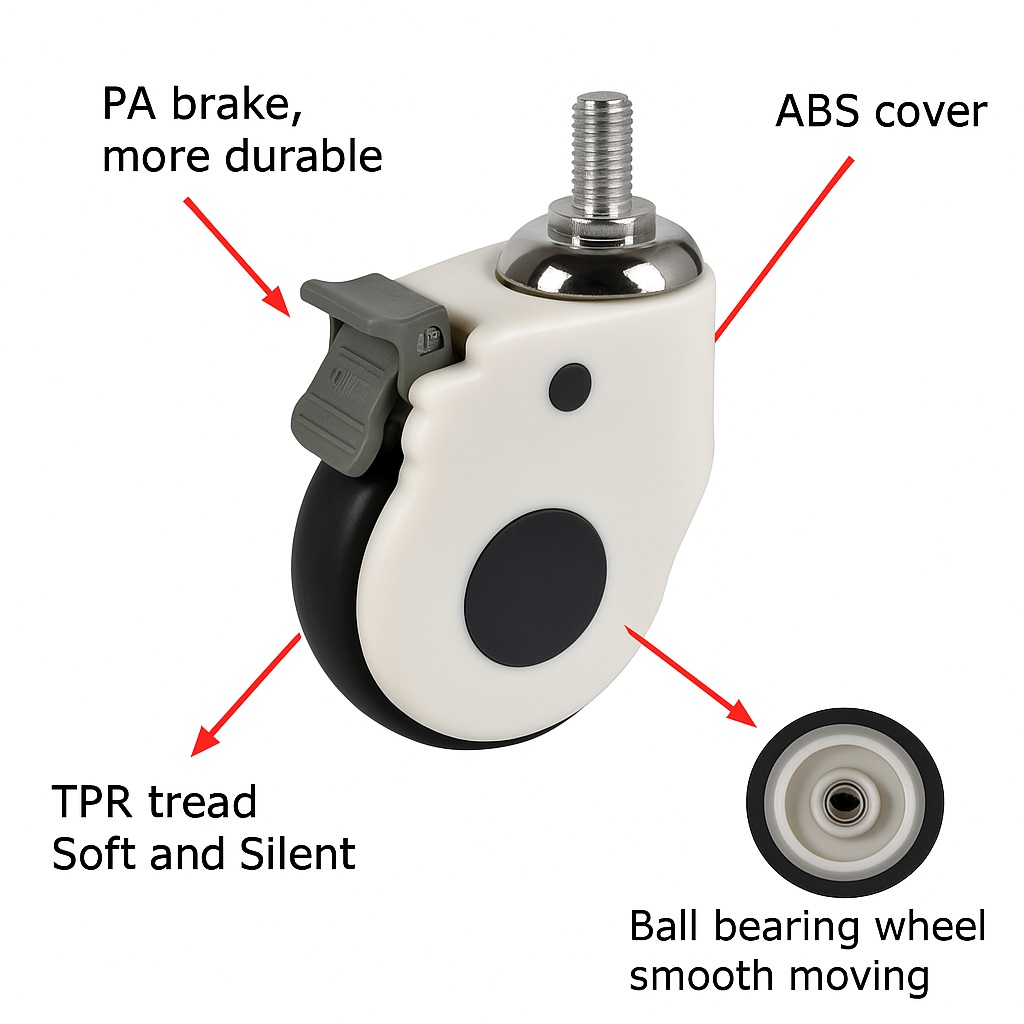
Not all castors are equal. Wheel diameter, tread material, and lock design change the performance.
Each choice fits a different scene. That’s why OEM/ODM is critical. Buyers want casters that match their beds, their floors, and their workflow. Our Hospital Bed Furniture range is built for this kind of matching.
Table: Advantages and limits of locking mechanisms
| Aspect | Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Safety | Stops unwanted rolling, prevents falls, protects patients | Locks wear down with time, need regular check |
| Efficiency | Staff push less, save time in alignment | Some locks too stiff, need redesign for ease |
| Compliance | Meets regulations, boosts hospital audit score | Old facilities may need upgrades |
| Cost | Fewer accidents, lower maintenance long-term | Higher upfront investment |
In a provincial hospital ICU, staff noticed that older beds without reliable locks often shifted when connecting monitoring devices. After switching to beds fitted with total-lock castors, the beds stayed firmly in place during line insertions. Nurses reported fewer interruptions, and patient handling became safer.
At a long-term care center, residents often moved between bed and wheelchair. Before, drifting beds created gaps and unsafe transfers. Installing castors with locking mechanisms solved this: once nurses tapped the pedal, the bed stopped completely. Residents felt more secure, and falls during transfer dropped to zero in quarterly reports.

In one large urban hospital, long hallways made bed transport exhausting. Directional-lock castors were added to reduce side drift. Porters shared feedback that they could push heavy beds with one hand while steering equipment with the other. The upgrade reduced the number of staff needed for transfers, cutting time and manpower.
These are daily, repeat uses. Locks aren’t a “feature.” They are tools for safety.
When hospital purchasing teams review tenders, they ask: “How do these castors reduce accident risk?” and “What about staff efficiency?” That’s the business side of safety.
For wholesale buyers and distributors, offering hospital beds with advanced castors makes the product stand out. It’s a way to deliver added value without redesigning the entire bed. Small parts, big impact.
Our HOSPITAL BED SOLUTIONS portfolio is made for this thinking: reliable hardware, OEM customization, and bulk supply to meet project scale.
Locks only work if staff use them right. That’s why hospitals combine training with regular checks. A sticky pedal, worn brake pad, or misaligned wheel can ruin the safety chain.
Procurement teams often add this in their RFPs: “easy maintenance and replacement.” It reduces downtime and keeps wards running.
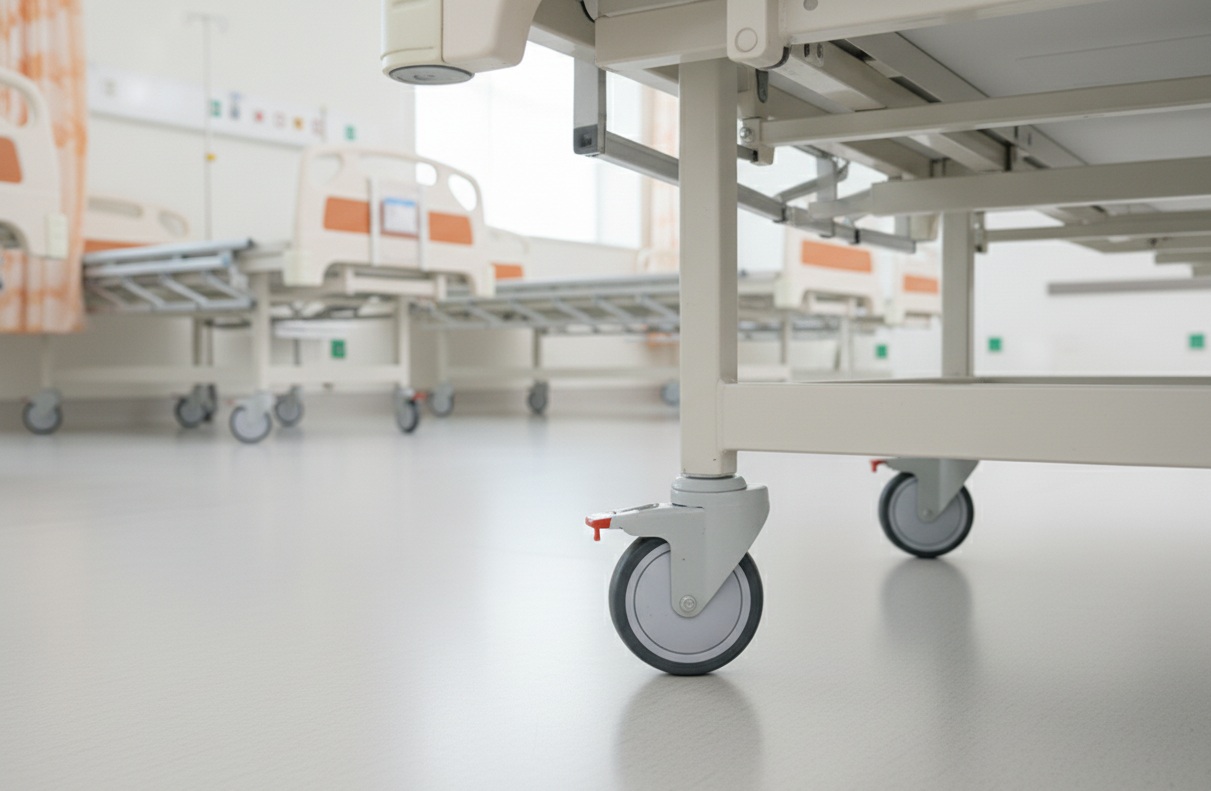
Hospital bed castors with locking mechanisms may look like simple add-ons. In practice, they shape safety, efficiency, and compliance across an entire facility.
When you source castors, you’re not just buying wheels. You’re investing in safer, smoother hospital operations.
Explore our Hospital Bed Castor solutions and see how OEM/ODM supply helps your business deliver both safety and commercial strength.